Introduction: Employee Health Insurance Plans
Employee health insurance is a critical part of any comprehensive benefits package. With rising healthcare costs and an increased focus on employee well-being, offering health insurance is no longer just an option for businesses—it’s a necessity. It plays a key role in attracting and retaining top talent, boosting morale, and ensuring the overall well-being of the workforce. In this post, we’ll explore what employee health insurance is, why it’s essential, the types of plans available, and how employers can choose the best option for their teams.
What is Employee Health Insurance?
Employee health insurance is a group insurance plan provided by employers to their employees, often including coverage for their families. This type of insurance helps cover medical expenses, such as doctor visits, hospital stays, surgeries, prescription drugs, and preventive care. By offering these benefits, employers provide a safety net that protects employees from the financial burden of unexpected medical costs, which can be overwhelming without adequate coverage.
Employers typically cover a portion of the premium costs, while employees contribute through payroll deductions. The specifics of coverage vary depending on the plan, but most include a range of services, from routine check-ups to emergency care.

Why is Employee Health Insurance Important?
- Attracting and Retaining Talent
In today’s competitive job market, comprehensive benefits like health insurance can make a company stand out. Many job seekers consider health insurance a non-negotiable benefit when choosing an employer. Offering competitive health insurance packages can help businesses attract and retain the best talent, reducing turnover and maintaining a productive workforce. - Boosting Employee Morale and Productivity
Employees who have access to good health insurance tend to feel more secure and valued by their employer. This sense of security reduces stress, leading to higher job satisfaction, increased morale, and greater productivity. Healthy employees are also less likely to miss work due to illness, which directly benefits the company’s bottom line. - Legal Requirements
In many countries, businesses of a certain size are required by law to provide health insurance to employees. In the U.S., for example, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) mandates that companies with 50 or more full-time employees offer health insurance or face penalties. Adhering to these regulations not only avoids legal repercussions but also shows that a company cares about the well-being of its employees. - Promoting Preventive Care
With health insurance, employees are more likely to seek preventive care, which can catch health issues early before they become serious or expensive to treat. Routine check-ups, vaccinations, and screenings are often covered, which leads to a healthier workforce in the long run.
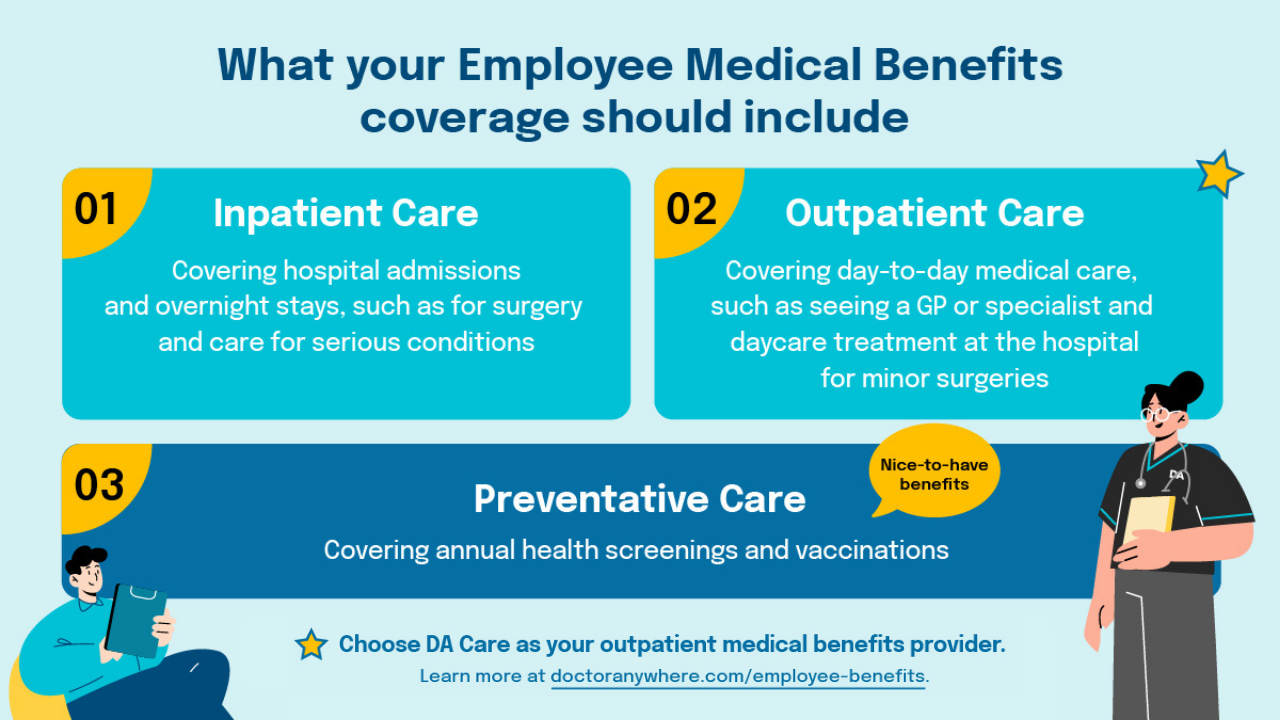
Types of Employee Health Insurance Plans
There are several types of employee health insurance plans, each offering different levels of coverage and flexibility. Employers need to understand these options to choose the best one for their workforce.
- Health Maintenance Organization (HMO)
HMOs are one of the most popular types of health insurance plans. They require employees to select a primary care physician (PCP) and receive referrals to see specialists. This type of plan tends to have lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs but limits employees to a network of healthcare providers. While this can reduce flexibility, it encourages preventive care and a close doctor-patient relationship. - Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)
PPOs offer more flexibility compared to HMOs. Employees can see any healthcare provider without needing a referral, although staying within a preferred network usually results in lower costs. PPO plans tend to have higher premiums, but they provide greater freedom in choosing doctors and specialists. - Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO)
EPO plans are similar to PPOs but with one key difference—employees must use the plan’s network of doctors and hospitals except in emergencies. This plan type is a middle ground, offering some flexibility but often at a lower cost than PPOs. - Point of Service (POS)
POS plans combine features of both HMOs and PPOs. Employees choose a primary care physician but can see out-of-network providers at a higher cost. Like an HMO, a referral is needed to visit specialists, but the ability to go outside the network gives employees more options. - High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) with Health Savings Account (HSA)
HDHPs have lower premiums but higher deductibles. They are often paired with an HSA, which allows employees to save money tax-free for medical expenses. This option is popular among younger, healthier employees who do not expect to have significant medical costs but want coverage in case of emergencies.

How to Choose the Right Health Insurance Plan for Your Employees
Choosing the right health insurance plan can be a daunting task for employers. There are several factors to consider to ensure the plan meets the needs of both the company and its employees:
- Understand Employee Needs
Conducting surveys or meetings with employees can help employers understand what they prioritize in a health plan. Younger employees may prefer lower premiums and higher deductibles, while older employees might seek comprehensive coverage with lower out-of-pocket costs. - Evaluate the Cost
While offering high-quality insurance is essential, it must also be affordable for both the employer and employees. Compare the premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and other costs across different plans to find one that offers good value without straining the company’s budget. - Consider Network Size and Accessibility
Ensure that the plan’s network includes hospitals, specialists, and doctors that are accessible to your employees. If the network is too limited, employees may face challenges accessing care, leading to dissatisfaction with the plan. - Balance Flexibility and Cost
Some employees may value the ability to choose their healthcare providers without restrictions, while others might prioritize lower costs. Finding a balance between these needs is key to selecting the best plan for the workforce.
The Future of Employee Health Insurance
As healthcare costs continue to rise, the landscape of employee health insurance is evolving. Many companies are exploring alternative ways to provide affordable coverage, such as telemedicine, wellness programs, and self-funded insurance plans. Telemedicine, for example, allows employees to consult with doctors remotely, reducing the need for in-person visits and lowering healthcare expenses. Similarly, wellness programs that encourage healthy lifestyles can help prevent chronic diseases, leading to long-term savings for both employers and employees.
Additionally, the growing emphasis on mental health is reshaping health insurance offerings. Employers are increasingly including mental health services, such as counseling and therapy, as part of their benefits packages to support the emotional well-being of their teams.
Conclusion
Employee health insurance is an invaluable benefit that helps companies attract top talent, boost morale, and ensure the well-being of their workforce. By understanding the different types of plans available and considering the unique needs of employees, businesses can choose a health insurance plan that benefits everyone. As healthcare evolves, staying informed about the latest trends and innovations will allow employers to offer competitive and effective coverage, promoting a healthier and more productive workplace.
FAQs
What is the difference between HMO and PPO plans?
HMO plans require a primary care physician and have a restricted network of providers, while PPO plans offer more flexibility in choosing doctors but often come with higher premiums.
How does a High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) work?
An HDHP has lower premiums but higher deductibles. It is often paired with a Health Savings Account (HSA) to help employees save for medical expenses.
Are employers legally required to offer health insurance?
In some countries, yes. For example, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) mandates that businesses with 50 or more full-time employees provide health insurance in the U.S.
What is an HSA, and how does it benefit employees?
A Health Savings Account (HSA) is a tax-advantaged account used to save for medical expenses. Employees with high-deductible health plans can contribute to an HSA and use the funds for healthcare costs.
How can employers choose the right health insurance plan?
Employers should consider factors like employee needs, cost, network size, and flexibility when choosing a plan.
What are the benefits of offering health insurance to employees?
Health insurance improves employee retention, increases productivity, and ensures legal compliance while promoting the overall health and well-being of the workforce.
